
What Is the Difference Between Medical and Biomedical Imaging?
Both medical and biomedical imaging are essential technologies that have helped transform healthcare and research. They’re both necessary for medical progression but are distinct in both approach and application.
Medical imaging is used for assessing, diagnosing and treating diseases in patients and provides medical professionals with detailed visualisations of internal structures.
Biomedical imaging, however, delves deeper into the study of biological processes at a cellular and molecular level. It aims to inform scientific understanding and develop advanced therapies.
While they differ in function and impact, these technologies often complement each other in the medical space. Let’s get into it.
What is Medical Imaging?
Medical imaging is primarily used to diagnose, monitor and treat medical conditions. It involves the use of various techniques and equipment to visualise the internal structures of the human body.
Common techniques in medical imaging include:
- X-ray: Commonly used to visualise the chest, airways, spine and bones.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This non-invasive technique produces detailed images of soft tissues such as the brain, muscles, and organs.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scans: Involves an x-ray examination to produce computer-generated, cross-sectional images of the inside of the body.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to capture images of organs, tissues, and blood flow, often used in prenatal care.
These techniques use advanced equipment to achieve a diagnosis. For example, MRI machines use powerful magnets, while CT scanners rely on rotating X-rays. These tools are essential for detecting conditions such as cancer, tumours and heart problems like cardiovascular disease and neurological disorders.
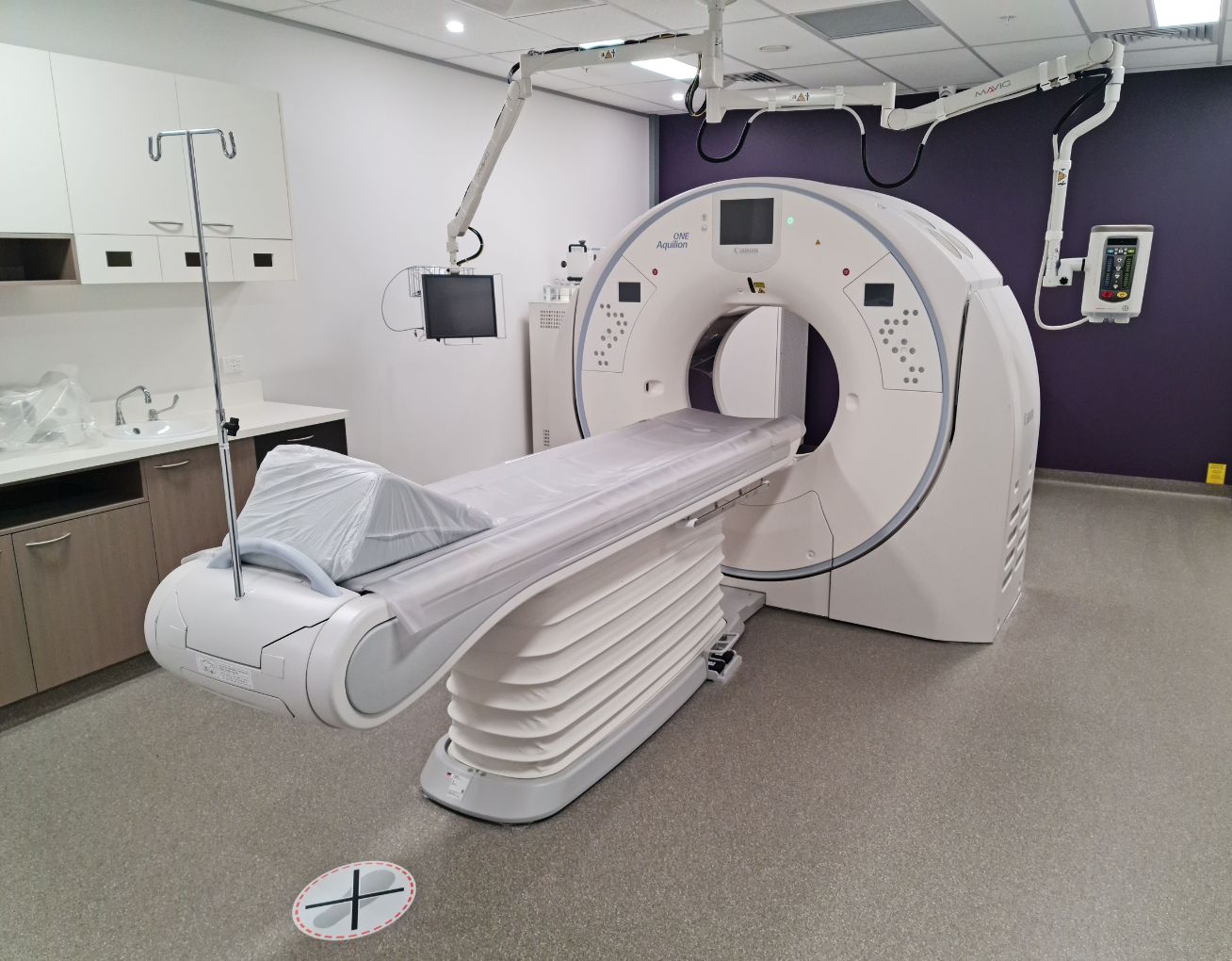
What is Biomedical Imaging?
Biomedical imaging focuses on the research side of imaging technology. The focus is on studying biological processes, understanding disease mechanisms, and developing new treatments.
Key techniques in the field of biomedical imaging include:
- fMRI (Functional MRI): Measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow.
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography) Scan: Tracks metabolic processes, often used in cancer research.
- Molecular Imaging: Allows researchers to visualise the behaviour of molecules within cells.
Biological imaging is crucial for scientific discovery, offering insight into how diseases like Alzheimer’s progress or how new medications interact with the systems of the body.
Key Differences Between Medical and Biomedical Imaging
Despite sharing some underlying principles, the purpose and applications of medical and biomedical imaging do differ.
Purpose: Medical imaging focuses on patient care, enabling disease detection, diagnosis and treatment. Biomedical imaging, however, is geared towards scientific discovery.
Techniques: Medical imaging often uses techniques like X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasounds for immediate clinical needs, whereas biomedical imaging employs research tools like fMRI and molecular imaging for deeper biological insights.
Application: In medical imaging, the primary goal is improving patient outcomes. Biomedical imaging seeks to advance scientific knowledge and develop innovative healthcare solutions.
Despite these differences, they both have advantages, and the two fields often complement each other, driving advancement and innovation in clinical care, analysis and research.
Overlap and Interdisciplinary Advances
Like many things in medicine, when the two work in harmony, great things happen. The overlap between medical and biomedical imaging has led to remarkable advancements in healthcare and research.
For example, molecular imaging techniques, initially developed to study metabolism and genomics, are now adapted to detect cancers at an early stage in clinical settings.
Similarly, medical imaging advances contribute to biomedical research. High-resolution MRI and CT scans, originally designed for diagnosing physiological conditions, are now applied in studies of biological processes, helping researchers explore the underlying mechanisms of health and disease.
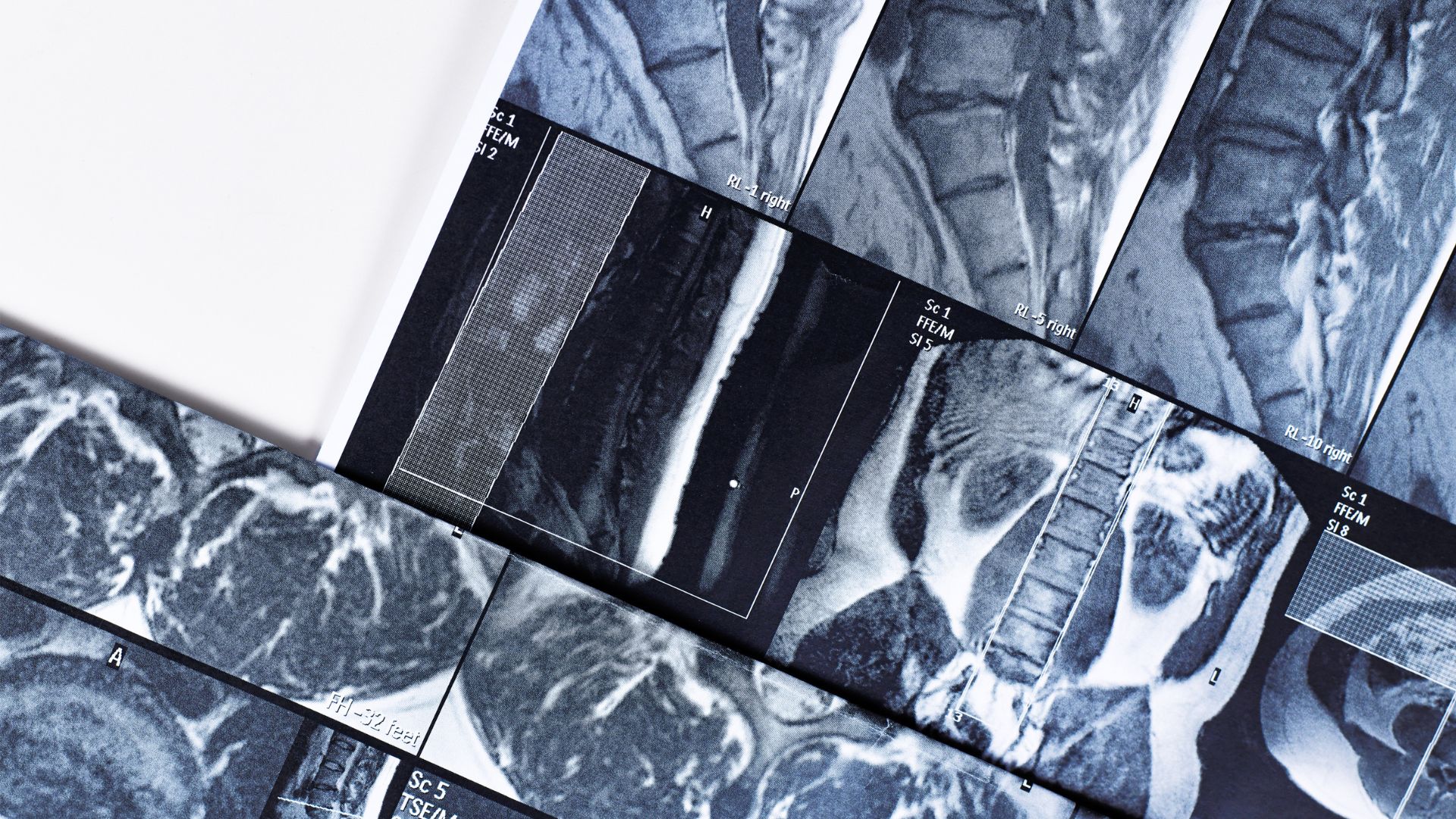
These imaging methods also improve the performance of radiology and other clinical results with precision and efficiency.
Future Trends in Imaging Technologies
The future of medical and biomedical imaging is bright! Medical imaging is evolving with AI-assisted diagnostics, portable imaging devices and energy-efficient imaging techniques, making healthcare more accessible and efficient.
Biomedical imaging methods enhance our ability to understand molecular dynamics, cellular processes and physiological performance, paving the way for new therapies and advancements in healthcare informatics.
As these technologies continue to merge, the line between medical and biomedical imaging blurs, which encourages wider collaboration across the two industries.
Book an Appointment with PRP Imaging
By recognising the unique roles of medical and biomedical imaging, we gain a deeper appreciation of how these technologies are shaping the future of healthcare and scientific exploration. Through constant training, doctors and radiologists ensure that the latest trends benefit every patient.
At PRP, we know how important it is to stay at the leading edge of technology and innovation. We’re passionate about medical technology, after all, it’s what we do best.
To explore our offerings further, or to book an imaging appointment with our friendly, expert medical professionals, get in touch with the PRP Imaging team today.
